Progressive Jackpot
Game Terpopuler
Promosi
Masuk Ke Dunia QQSLOT Autentik Melalui Link Alternatif Resmi: Kepuasan dan Kemenangan Tanpa Batas Menanti Anda
Kenalan Yuk dengan QQSLOT dan Penawarannya yang Top Banget!
Halo bro sis! Welcome to QQSLOT, pintu masuk lo ke dunia game online yang menjamin keseruan dan kemenangan yang gede banget. Sebagai tempat judi online yang paling hits, QQSLOT punya macem-macem game yang dirancang khusus buat memenuhi selera beragam pemain kita. Mulai dari slot yang bikin adrenalin lo naik, sampe e-games yang seru abis, semua disajikan dengan keamanan dan keaslian yang top dan tentunya pasti aman dan bisa dipercaya, link kami adalahh link anti nawala
Qqslot Situs link daftar dan link login yang memiliki server terbaik sehingga pada tahun ini sebagai situs tergacor yang selalu ada di Asia sampai sekarang ini. Memberikan kemenangan setiap hari nya kepada para member baru tanpa harus terapkan pola apapun.
Gimana Sih QQSLOT Jamin Keaslian dan Keamanan Game?
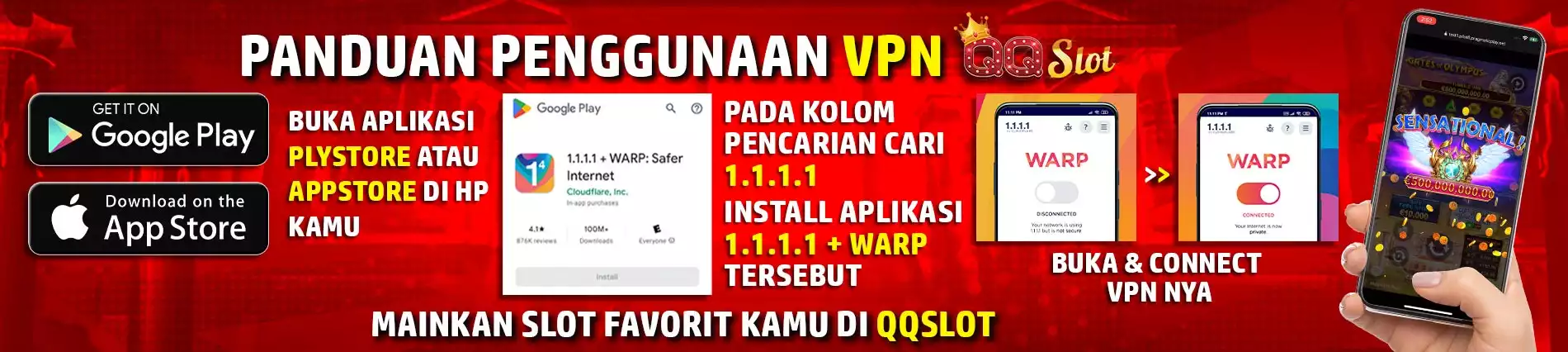
Di QQSLOT, keamanan itu prioritas utama kita. Platform kita dilengkapi dengan teknologi keamanan paling canggih buat memastikan kenyamanan dan keamanan bermain kamu. Lo bakal main dengan tenang karena kita cuma pake link resmi buat akses, yang melindungi dari bahaya phishing atau scam. Untuk itu hanya main di situs yang sudah terpercaya yaitu QQSLOT yang domain nya bisa diakses dari qqslot.com via VPN yang akan ter-redirect ke domain ini sekarang karena domain ini adalah domain authentic / asli yang dimiliki oleh situs QQSLOT yang asli dari platform MPOPLAY sejak 10 tahun lalu
Cek Yuk, Berbagai Game yang Bisa Lo Mainin di QQSLOT
QQSLOT menawarkan macem-macem permainan, termasuk:
- Slot Games: Nikmati berbagai slot dengan tema unik dan gameplay yang keren.
- E-Games: Rasakan game elektronik terbaru yang mix antara tradisional dan modern.
- Table Games: Mainkan game klasik kasino seperti poker, blackjack, dan roulette.
Jelajahi Pilihan Game Seru di QQSLOT
Platform kita punya game dari developer top seperti Pragmatic Play dan Habanero di platform qqslot online yang menjamin grafis berkualitas dan pengalaman yang immersive.
Slot Games yang Wajib Dicoba di QQSLOT
Coba deh game di platform qqslot populer seperti "Starburst" atau "Book of Dead" yang punya grafis mantap dan tema yang menarik.
E-Games Eksklusif dan Fitur-fitur Menariknya
Temukan e-games eksklusif yang hanya ada di QQSLOT, dirancang buat memanjakan dan menghibur setiap pemain.
Tips Maximalkan Peluang Menang Lo di QQSLOT
Pelajari strategi buat meningkatkan permainan lo dan tingkatin kesempatan lo buat dapetin jackpot besar di QQSLOT.
Pentingnya Pake Link Alternatif Resmi Buat Akses QQSLOT
Menggunakan link resmi itu penting banget buat memastikan lo masuk ke platform QQSLOT yang asli, jadi data lo aman dan pengalaman bermain lo lancar.
Kenapa Sih Link Resmi Itu Lebih Aman?
Link resmi itu sudah diverifikasi dan dijamin aman, menghilangkan risiko phishing dan ancaman online lainnya.
Panduan Gampang Akses QQSLOT lewat Link Resmi
Ikuti panduan simpel dari kita buat akses secara aman ke semua game dan fitur yang ditawarkan QQSLOT.
Komitmen QQSLOT Buat Kepuasan dan Keamanan Pengguna
Kita selalu utamakan kepuasan dan keamanan pengguna, jadi pengalaman bermain lo dijamin transparan dan aman.
Proses Transaksi yang Transparan di QQSLOT
Mengerti deh proses transaksi kita yang simpel, dirancang buat transaksi finansial yang cepat dan jelas.
Layanan Pelanggan dan Dukungan di QQSLOT
Tim support kita yang ramah dan profesional siap membantu lo dengan segala pertanyaan atau masalah yang mungkin muncul.
Cara Hubungi Dukungan dan Dapatkan Bantuan
Pelajari cara-cara terbaik buat kontak tim support qqslot online asli kita buat bantuan yang cepat dan efektif.
Tips Buat Pengalaman Bermain QQSLOT yang Lancar
Dapetin tips-tips praktis buat meningkatkan pengalaman bermain lo di QQSLOT.
Kesimpulan
QQSLOT itu kayak mercusuar buat fun, keamanan, dan peluang menang yang gede. Dengan link yang aman dan desain yang fokus pada user, tiap kunjungan lo bakalan terasa kayak masuk ke dunia kesempatan yang luas. Ayo gabung sekarang dan mulai petualangan lo untuk menang besar!
FAQ
- Gimana caranya biar pasti pake link resmi QQSLOT?
- Apa aja sih permainan paling ngetop di QQSLOT?
- Gimana cara hubungi customer service kalo ada masalah?
- Apa aja keuntungan main di QQSLOT?
- Gimana QQSLOT jamin keamanan permainannya?
- Bisa main di QQSLOT dari perangkat apa aja gak?
Nah, itu dia ulasan mengenai situs qqslot yang asli dimana kalian bisa bermain dengan tenang dan aman karena kami menjamin semuanya.
Sistem Pembayaran






















Perhatian.
KLAIM BONUS 100% DENGAN TURNOVER SUPER KECIL DISINI
============================================
DEPOSIT INSTAN QRID PROSES DEPOSIT HANYA 3 DETIK
Pertama di Indonesia Proses Deposit Tercepat 3 Detik Auto Gacor, Tanpa Potongan / Biaya
Tersedia Untuk Semua Bank lokal - E-wallet
Dari Pada Tunggu Lama Yuk QRID Saja.
============================================
Link ALTERANTIF : https://play3.qqslot.in/
Link AMPLOP : https://play1.qqslotprize.com/
Link DEPO STREAK : https://qqslotevent.net/depositstreak
============================================
Deposit Lewat Mesin EDC Akan Di Proses Setelah 1 x 24 Jam
Pastikan rekening tujuan sebelum mengirim, jika ada kesalahan itu bukan tanggung jawab kami.
Formulir Login

VERIFICATION NOTICE
- I am agree to qqslot's term and condition.
- I am over the age of 21 and will comply with the above statement.
By entering this website, you acknowledge and confirm: